Description
Mitochondrial markers are structural or functional properties that are specific for mitochondria. A structural mt-marker is the area of the inner mt-membrane or mt-volume determined stereologically, which has its limitations due to different states of swelling. If mt-area is determined by electron microscopy, the statistical challenge has to be met to convert area into a volume. When fluorescent dyes are used as mt-marker, distinction is necessary between mt-membrane potential dependent and independent dyes. mtDNA or cardiolipin content may be considered as a mt-marker. Mitochondrial marker enzymes may be determined as molecular (amount of protein) or functional properties (enzyme activities). Respiratory capacity in a defined respiratory state of a mt-preparation can be considered as a functional mt-marker, in which case respiration in other respiratory states is expressed as flux control ratios. » MiPNet article
Abbreviation: mt-marker
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
Mitochondrial markers and expression of mitochondrial respiration
| Gnaiger E (2014) Mitochondrial markers and expression of mitochondrial respiration. Mitochondr Physiol Network 2014-07-26. |
Abstract: Respiratory performance capacity of an organism, tissue or cell may change due to a change in size, concentration of functional elements (biomarker density) or element function (mt-specific function).
• O2k-Network Lab: AT Innsbruck Gnaiger E
Biomarkers
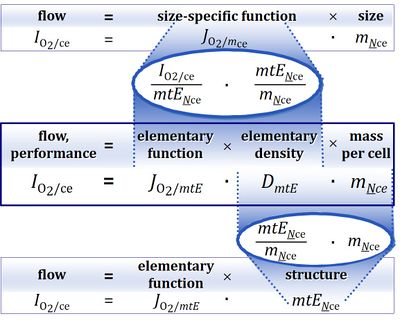
- Markers for size are volume, mass, area. If mass is not expressed as total mass but as protein mass, then a physical marker of size is replaced by a biochemical marker. In isolated mitochondria, protein can be determined as a measure of amount of mitochondria or mt-concentration [mg mt-protein/mL]. However, protein cannot be used as a mt-biomarker in other mitochondrial preparations.
- Determination of the size of a system under investigation always requires the definition of the system. The system (subject) whose phenotype is studied may be an organism, a tissue, or a cell. The biochemical marker total protein can be replaced by a specific protein, e.g. by a marker enzyme (Renner et al 2003). A biomarker can be considered as a functional element. Expressing performance (IO2, oxygen flow per biological system) per size yields specific performance (JO2, oxygen flux = flow per system size) in an unstructured analysis (Gnaiger 1993).
- A biomarker introduces a structural (and functional) element into the analysis. Therefore, expressing performance (IO2) per functional element mtE (biomarker) yields marker-specific performance (JO2/mtE, mt-specific oxygen flux per mt-marker) in a structured analysis (Gnaiger 2020).
- When replacing an enzyme activity by the respiratory activity in a defined respiratory state as a biomarker, then flow per mt-marker becomes a flux control ratio FCR (Gnaiger 2009; Pesta et al 2011). Expressing structure by functional markers is without problem as long as the structure in question does not undergo any functional (qualitative) changes.
References
| Bioblast link | Reference | Year |
|---|---|---|
| Gnaiger 1993 Pure Appl Chem | Gnaiger E (1993) Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of energy transformations. Pure Appl Chem 65:1983-2002. http://dx.doi.org/10.1351/pac199365091983 | 1993 |
| Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol | Gnaiger E (2009) Capacity of oxidative phosphorylation in human skeletal muscle. New perspectives of mitochondrial physiology. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2009.03.013 | 2009 |
| Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways | Gnaiger E (2020) Mitochondrial pathways and respiratory control. An introduction to OXPHOS analysis. 5th ed. Bioenerg Commun 2020.2. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0002 | 2020 |
| BEC 2020.1 doi10.26124bec2020-0001.v1 | Gnaiger E et al ― MitoEAGLE Task Group (2020) Mitochondrial physiology. Bioenerg Commun 2020.1. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2020-0001.v1 | 2020 |
| Pesta 2011 Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol | Pesta D, Hoppel F, Macek C, Messner H, Faulhaber M, Kobel C, Parson W, Burtscher M, Schocke M, Gnaiger E (2011) Similar qualitative and quantitative changes of mitochondrial respiration following strength and endurance training in normoxia and hypoxia in sedentary humans. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 301:R1078–87. | 2011 |
| Renner 2003 Biochim Biophys Acta | Renner K, Amberger A, Konwalinka G, Gnaiger E (2003) Changes of mitochondrial respiration, mitochondrial content and cell size after induction of apoptosis in leukemia cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1642:115-23. | 2003 |
- Bioblast links: Normalization - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Quantities for normalization
- » Count in contrast to Number
- » Mitochondrial marker
- » O2k-Protocols: mitochondrial and marker-enzymes
- » Citrate synthase activity
- Quantities for normalization
- General
- Related keyword lists
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry,
Fluorometry,
Spectrophotometry
MitoPedia topics:
Enzyme
Labels: MiParea: Respiration
Regulation: Flux control
HRR: Theory

