Liufu 2023 Front Physiol
| Liufu T, Yu H, Yu J, Yu M, Tian Y, Ou Y, Deng J, Xing G, Wang Z (2023) Complex I deficiency in m.3243A>G fibroblasts is alleviated by reducing NADH accumulation. Front Physiol 14:1164287. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2023.1164287 |
Liufu T, Yu H, Yu J, Yu M, Tian Y, Ou Y, Deng J, Xing G, Wang Z (2023) Front Physiol
Abstract: Introduction: Mitochondrial disease is a spectrum of debilitating disorders caused by mutations in the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) or nuclear DNA that compromises the respiratory chain. Mitochondrial 3243A>G (m.3243 A>G) is the most common mutation showing great heterogeneity in phenotype. Previous studies have indicated that NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) deficiency accompanied by a decreased nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)/reduced NAD+ (NADH) ratio may play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of m.3243A>G mutation. Methods: To evaluate the potential effects of strategies targeting the imbalanced NAD+/NADH ratio in m.3243A>G mutation, we treated fibroblasts derived from patients with the m.3243 A>G mutation using nicotinamide riboside (NR) or mitochondria-targeted H2O-forming NADH oxidase (mitoLbNOX). Results: M.3243 A>G fibroblasts showed a significant reduction in complex I core subunit 6, complex I enzymatic activity, complex I-dependent oxygen consumption rate (OCR), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production compared to the controls. The NAD+/NADH ratio was also significantly reduced in m.3243 A>G fibroblasts, and, using fluorescence lifetime imaging microscopy, we also found that the NADH level was elevated in m.3243 A>G fibroblasts. After NR treatment, the NAD+/NADH ratio, complex I-dependent OCR, and ATP levels increased, whereas NADH levels remained unchanged. More excitingly, after treatment with mitoLbNOX, the NAD+/NADH ratio, complex I-independent OCR, and ATP levels increased more pronouncedly compared with the NR treatment group, accompanied by significantly reduced NADH levels. Discussion: The present study suggests that compared with repletion of NAD+ alone, the combination of this therapeutic modality with alleviation of NADH overload may amplify the treatment effect of restoring NAD+/NADH balance in m.3243A>G fibroblasts.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
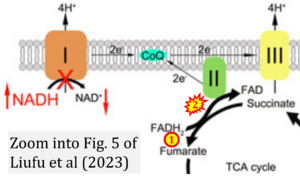
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«