Perouansky 2023 Exp Biol Med (Maywood)
| Perouansky M, Johnson-Schlitz D, Sedensky MM, Morgan PG (2023) A primordial target: Mitochondria mediate both primary and collateral anesthetic effects of volatile anesthetics. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 248:545-52. https://doi.org/10.1177/15353702231165025 |
Perouansky M, Johnson-Schlitz D, Sedensky MM, Morgan PG (2023) Exp Biol Med (Maywood)
Abstract: One of the unsolved mysteries of medicine is how do volatile anesthetics (VAs) cause a patient to reversibly lose consciousness. In addition, identifying mechanisms for the collateral effects of VAs, including anesthetic-induced neurotoxicity (AiN) and anesthetic preconditioning (AP), has proven challenging. Multiple classes of molecules (lipids, proteins, and water) have been considered as potential VA targets, but recently proteins have received the most attention. Studies targeting neuronal receptors or ion channels had limited success in identifying the critical targets of VAs mediating either the phenotype of "anesthesia" or their collateral effects. Recent studies in both nematodes and fruit flies may provide a paradigm shift by suggesting that mitochondria may harbor the upstream molecular switch activating both primary and collateral effects. The disruption of a specific step of electron transfer within the mitochondrion causes hypersensitivity to VAs, from nematodes to Drosophila and to humans, while also modulating the sensitivity to collateral effects. The downstream effects from mitochondrial inhibition are potentially legion, but inhibition of presynaptic neurotransmitter cycling appears to be specifically sensitive to the mitochondrial effects. These findings are perhaps of even broader interest since two recent reports indicate that mitochondrial damage may well underlie neurotoxic and neuroprotective effects of VAs in the central nervous system (CNS). It is, therefore, important to understand how anesthetics interact with mitochondria to affect CNS function, not just for the desired facets of general anesthesia but also for significant collateral effects, both harmful and beneficial. A tantalizing possibility exists that both the primary (anesthesia) and secondary (AiN, AP) mechanisms may at least partially overlap in the mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC).
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
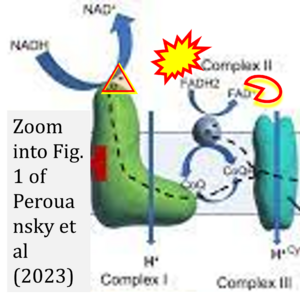
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Hydrogen ion ambiguities in the electron transfer system
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2023-10-08) last update 2023-11-10
- Electron (e-) transfer linked to hydrogen ion (hydron; H+) transfer is a fundamental concept in the field of bioenergetics, critical for understanding redox-coupled energy transformations.
- However, the current literature contains inconsistencies regarding H+ formation on the negative side of bioenergetic membranes, such as the matrix side of the mitochondrial inner membrane, when NADH is oxidized during oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS). Ambiguities arise when examining the oxidation of NADH by respiratory Complex I or succinate by Complex II.
- Oxidation of NADH or succinate involves a two-electron transfer of 2{H++e-} to FMN or FAD, respectively. Figures indicating a single electron e- transferred from NADH or succinate lack accuracy.
- The oxidized NAD+ is distinguished from NAD indicating nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide independent of oxidation state.
- NADH + H+ → NAD+ +2{H++e-} is the oxidation half-reaction in this H+-linked electron transfer represented as 2{H++e-} (Gnaiger 2023). Putative H+ formation shown as NADH → NAD+ + H+ conflicts with chemiosmotic coupling stoichiometries between H+ translocation across the coupling membrane and electron transfer to oxygen. Ensuring clarity in this complex field is imperative to tackle the apparent ambiguity crisis and prevent confusion, particularly in light of the increasing number of interdisciplinary publications on bioenergetics concerning diagnostic and clinical applications of OXPHOS analysis.
Labels: MiParea: Pharmacology;toxicology
Organism: Human, Drosophila, Caenorhabditis elegans