Description
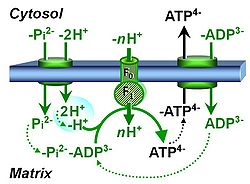
The phosphorylation pathway (phosphorylation system) is the functional unit utilizing the protonmotive force to phosphorylate ADP (D) to ATP (T), and may be defined more specifically as the P»-system. The P»-system consists of adenine nucleotide translocase, phosphate carrier, and ATP synthase. Mitochondrial adenylate kinase, mt-creatine kinase and mt-hexokinase constitute extended components of the P»-system, controlling local AMP and ADP concentrations and forming metabolic channels. Since substrate-level phosphorylation is involved in the TCA-cycle, the P»-system includes succinyl-CoA ligase (GDP to GTP or ADP to ATP).
Abbreviation: DT
Reference: Gnaiger 2009 Int J Biochem Cell Biol
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
SUIT concept
MitoPedia topics:
Enzyme
Communicated by Gnaiger E (2010-08-15) last update 2020-06-02.
OXPHOS and substrate-level phosphorylation
- OXPHOS capacity, measured as oxygen flux in coupled, ADP- and Pi-saturated mitochondria in an electron-transfer-pathway state, may be limited by the capacity of the phosphorylation system. Mitochondria are the location of the chemiosmotic P»-system, but additionally carry out substrate-level phosphorylation in the TCA-cycle at the step of succinyl-CoA ligase, phosphorylating GDP to GTP or ADP to ATP (taken together as P»). This step must be considered in the P»-system. If succinate is externally added to mt-preparations, succinyl-CoA ligase is not involved. However, if succinate is formed in the mt-matrix from 2-oxoglutarate (alpha-ketoglutarate), substrate-level phosphorylation at succinyl-CoA ligase must be accounted for in the interpretation of P/O2 ratios.