Prasun 2020 J Diabetes Metab Disord
| Prasun P (2020) Role of mitochondria in pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab Disord 19:2017-22. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-020-00679-x |
Prasun P (2020) J Diabetes Metab Disord
Abstract: Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is global health problem. An estimated 425 million people in the world had diabetes in 2017. It is a major cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Although, pathogenesis of T2DM and its complications have been focus of medical research for long, much remains to be learned. A better understanding of molecular pathogenesis is essential for more effective preventive and therapeutic interventions. Role of mitochondria in pathogenesis of metabolic problems such as obesity, metabolic syndrome, and T2DM is the focus of many recent research studies. Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the oxidative stress and systemic inflammation leading to insulin resistance (IR). Mitochondria are also essential for pancreatic beta cell insulin secretion. Hence, mitochondria are important players in the pathogenesis of T2DM. In this article, pathogenesis of T2DM is examined from a mitochondrial perspective.
• Bioblast editor: Gnaiger E
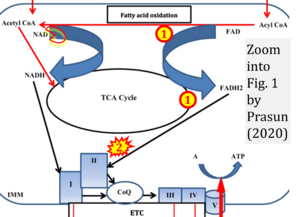
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels: Pathology: Diabetes