Cojocaru 2023 Antioxidants (Basel): Difference between revisions
(Created page with "{{Publication |title=Cojocaru KA, Luchian I, Goriuc A, Antoci LM, Ciobanu CG, Popescu R, Vlad CE, Blaj M, Foia LG (2023) Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and thera...") |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
|abstract=Mitochondria are subcellular organelles involved in essential cellular functions, including cytosolic calcium regulation, cell apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species production. They are the site of important biochemical pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid cycle, parts of the ureagenesis cycle, or haem synthesis. Mitochondria are responsible for the majority of cellular ATP production through OXPHOS. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been associated with metabolic pathologies such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, neurodegenerative diseases, cellular aging, and cancer. In this article, we describe the pathophysiological changes in, and mitochondrial role of, metabolic disorders (diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease) and their correlation with oxidative stress. We highlight the genetic changes identified at the mtDNA level. Additionally, we selected several representative biomarkers involved in oxidative stress and summarize the progress of therapeutic strategies. | |abstract=Mitochondria are subcellular organelles involved in essential cellular functions, including cytosolic calcium regulation, cell apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species production. They are the site of important biochemical pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid cycle, parts of the ureagenesis cycle, or haem synthesis. Mitochondria are responsible for the majority of cellular ATP production through OXPHOS. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been associated with metabolic pathologies such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, neurodegenerative diseases, cellular aging, and cancer. In this article, we describe the pathophysiological changes in, and mitochondrial role of, metabolic disorders (diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease) and their correlation with oxidative stress. We highlight the genetic changes identified at the mtDNA level. Additionally, we selected several representative biomarkers involved in oxidative stress and summarize the progress of therapeutic strategies. | ||
}} | }} | ||
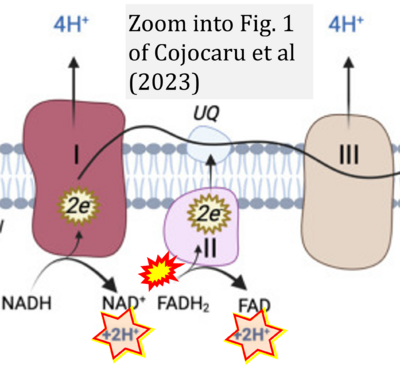
[[File:Cojocaru 2023 Antioxidants (Basel) CORRECTION.png|right|400px]] | |||
{{Template:Correction FADH2 and S-pathway}} | |||
{{Labeling | {{Labeling | ||
|diseases=Cardiovascular, Diabetes, Obesity | |diseases=Cardiovascular, Diabetes, Obesity | ||
| Line 12: | Line 14: | ||
|enzymes=Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase | |enzymes=Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 21:54, 28 September 2023
| Cojocaru KA, Luchian I, Goriuc A, Antoci LM, Ciobanu CG, Popescu R, Vlad CE, Blaj M, Foia LG (2023) Mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, and therapeutic strategies in diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 12(3):658. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030658 |
Cojocaru KA, Luchian I, Goriuc A, Antoci LM, Ciobanu CG, Popescu R, Vlad CE, Blaj M, Foia LG (2023) Antioxidants (Basel)
Abstract: Mitochondria are subcellular organelles involved in essential cellular functions, including cytosolic calcium regulation, cell apoptosis, and reactive oxygen species production. They are the site of important biochemical pathways, including the tricarboxylic acid cycle, parts of the ureagenesis cycle, or haem synthesis. Mitochondria are responsible for the majority of cellular ATP production through OXPHOS. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been associated with metabolic pathologies such as diabetes, obesity, hypertension, neurodegenerative diseases, cellular aging, and cancer. In this article, we describe the pathophysiological changes in, and mitochondrial role of, metabolic disorders (diabetes, obesity, and cardiovascular disease) and their correlation with oxidative stress. We highlight the genetic changes identified at the mtDNA level. Additionally, we selected several representative biomarkers involved in oxidative stress and summarize the progress of therapeutic strategies.
Correction: FADH2 and Complex II
- FADH2 is shown as the substrate feeding electrons into Complex II (CII). This is wrong and requires correction - for details see Gnaiger (2024).
- Gnaiger E (2024) Complex II ambiguities ― FADH2 in the electron transfer system. J Biol Chem 300:105470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105470 - »Bioblast link«
Labels: Pathology: Cardiovascular, Diabetes, Obesity Stress:Oxidative stress;RONS
Enzyme: Complex II;succinate dehydrogenase