Difference between revisions of "Superoxide"
From Bioblast
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
|abbr=O<sub>2</sub><sup>-•</sup> | |abbr=O<sub>2</sub><sup>-•</sup> | ||
|description=[[File:O2-.jpg|left|60px|Superoxide anion]] | |description=[[File:O2-.jpg|left|60px|Superoxide anion]] | ||
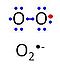
'''Superoxide anion''', O<sub>2</sub><sup>- | '''Superoxide anion''', O<sub>2</sub><sup>•-</sup>, is a free radical formed in a one-electron reduction of molecular [[oxygen]] (red bullet in the figure), yielding a negatively charged molecule with a single unpaired electron (blue bullet on the left). It is highly reactive with organic compounds, and its intracellular concentration is kept under control by [[superoxide dismutase]]. | ||
|info=[[Fridovich_1997_J Biol Chem]] | |||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia methods}} | {{MitoPedia methods}} | ||
Revision as of 03:56, 16 April 2014
Description
Superoxide anion, O2•-, is a free radical formed in a one-electron reduction of molecular oxygen (red bullet in the figure), yielding a negatively charged molecule with a single unpaired electron (blue bullet on the left). It is highly reactive with organic compounds, and its intracellular concentration is kept under control by superoxide dismutase.
Abbreviation: O2-•
Reference: Fridovich_1997_J Biol Chem
MitoPedia topics: Substrate and metabolite