From Bioblast
Description
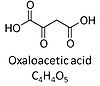
Oxaloacetic acid, C4H4O5, occurs under physiological conditions as the anion oxaloacetate2-, Oa. Oxaloacetate is formed from malate by MDH. Oa reacts with acetyl-CoA through citrate synthase to form citrate, or with glutamate through transaminase to form oxoglutarate and aspartate. Oa transport is restricted across the inner mt-membrane of various tissues. Oa is a potent inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase.
Abbreviation: Oa
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite