Difference between revisions of "Amount of substance"
From Bioblast
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
|info=[[Cohen 2008 IUPAC Green Book]] | |info=[[Cohen 2008 IUPAC Green Book]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Communicated by [[Gnaiger E]] 2018-11-01 | |||
== Changes of amount == | |||
:::: The amount of substance ''i'', ''n''<sub>''i''</sub>, contained in a system changes due to internal and external transformations, | |||
d''n''<sub>''i''</sub> = d<sub>i</sub>''n''<sub>''i''</sub> + d<sub>e</sub>''n''<sub>''i''</sub> | |||
:::: [[File:Amount dn.png|100px]] | |||
:::: The change of amount of ''i'' in an open system is due to internal formation in chemical transformations, where d<sub>r</sub>''n''<sub>''i''</sub> is positive if ''i'' is formed as a product of the reaction and the external transfer of substance ''i'', d<sub>e</sub>''n''<sub>''i''</sub> (negative if ''i'' flows out of the system and appears as a product in the surroundings [1]. | |||
== References == | |||
:::# Gnaiger E (1993) Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of energy transformations. Pure Appl Chem 65:1983-2002. - [[Gnaiger 1993 Pure Appl Chem |»Bioblast link«]] | |||
{{MitoPedia concepts | {{MitoPedia concepts | ||
|mitopedia concept=MiP concept, Ergodynamics | |mitopedia concept=MiP concept, Ergodynamics | ||
Revision as of 18:24, 1 November 2018
Description
The amount of substance, n, is a base physical quantity, and the corresponding SI unit is the mole [mol]. Amount of substance (sometimes abbreviated as 'amount' or 'chemical amount') is proportional to the number of specified elementary entities of that substance, and the universal proportionality constant is the reciprocal value of the Avogadro constant.
Abbreviation: n
Reference: Cohen 2008 IUPAC Green Book
Communicated by Gnaiger E 2018-11-01
Changes of amount
- The amount of substance i, ni, contained in a system changes due to internal and external transformations,
dni = dini + deni
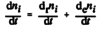
- The change of amount of i in an open system is due to internal formation in chemical transformations, where drni is positive if i is formed as a product of the reaction and the external transfer of substance i, deni (negative if i flows out of the system and appears as a product in the surroundings [1].
References
- Gnaiger E (1993) Nonequilibrium thermodynamics of energy transformations. Pure Appl Chem 65:1983-2002. - »Bioblast link«
MitoPedia concepts: MiP concept, Ergodynamics
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite
