Difference between revisions of "Cytochrome c"
| (47 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia | ||
|abbr=c | |abbr=c | ||
|description='''Cytochrome ''c''''' is a component of the | |description='''Cytochrome ''c''''' is a component of the Electron transfer-pathway ([[Electron transfer pathway]]) in mitochondria. It is a small heme protein loosely associated with the outer side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. The heme group of cytochrome ''c'' transfers electrons from [[Complex III]] to [[Complex IV]]. The release of cytochrome ''c'' into the cytoplasm is associated with apoptosis. Cytochrome ''c'' is applied in [[HRR]] to test the integrity of the [[mitochondrial outer membrane]] ([[cytochrome c control efficiency]]). | ||
|info=[[MiPNet09.12]]; [[Gnaiger 2002 Biochem Soc Trans]] | |info=[[MiPNet09.12]]; [[Gnaiger 2002 Biochem Soc Trans]] | ||
|methods_type=Substrate ETS | |||
}} | |||
{{MitoPedia concepts}} | |||
{{MitoPedia methods | |||
|type=Substrate ETS | |type=Substrate ETS | ||
}} | }} | ||
{{MitoPedia | {{MitoPedia O2k and high-resolution respirometry}} | ||
}} | |||
{{MitoPedia topics | {{MitoPedia topics | ||
|mitopedia topic=Substrate and metabolite | |mitopedia topic=Substrate and metabolite | ||
}} | }} | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Application in [[HRR]]: storage and stock solution of ''c'' == | == Application in [[HRR]]: storage and stock solution of ''c'' == | ||
''' ''c'': Cytochrome ''c'' ''' (from equine heart), Sigma C 7752, 50 mg, store at -20 °C; | {{Chemical_description | ||
|abbr=c | |||
|trivial name=Cytochrome ''c'' | |||
''' | |complete name=from equine heart | ||
|chem formula=small hemeprotein | |||
:: | |molar mass=12,384 | ||
|vendor=Sigma-Aldrich | |||
: | |product number=C7752 | ||
|store at=-20 °C | |||
|sensitivity= | |||
|cas=9007-43-6 | |||
|h statements= | |||
|h info= | |||
}}<!--::: '''''c'': Cytochrome ''c'' ''' (from equine heart), Sigma C 7752, 50 mg, store at -20 °C; MW = 12,384 Da.:::: <span style="color:#8B008B"> '''Caution:''' Chemicals stored in the fridge or freezer should be allowed to reach room temperature before opening. </span>-->::::<span style="color:#2E8B4F">The cytochrome ''c'' recommended (C7752, cytochrome ''c'' from equine heart) is out of stock for the next months (estimated delivery on [https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/AT/en/product/sigma/c7752?context=product November 25, 2021]). The use of other cytochrome ''c'' sources is discussed in the [[Talk:Cytochrome_c|MiPNet discussion forum]].</span> | |||
''' | :::: '''Preparation of 4 mM cytochrome ''c'' solution''' (dissolved in H<sub>2</sub>O) for '''2-mL O2k-chamber''': | ||
:: | ::::# Weigh 50 mg cytochrome ''c'' into a small glass beaker. Difficult to weigh, since the powder is electrostatically charged. | ||
:: | ::::# Add 1 mL H<sub>2</sub>O; ''c'' dissolves easily. | ||
::::# Divide into 0.2 mL portions. | |||
::::# Store at -20 °C. | |||
:::» '''O2k manual titrations:''' [[MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations]] | |||
::::* Titration volume ('''2-mL O2k-chamber'''): 5 µL using a 25 µL Hamilton syringe. | |||
::::* Final concentration: 10 µM. | |||
:::: '''Preparation of 5 mM cytochrome ''c'' solution''' (dissolved in H<sub>2</sub>O) for '''0.5-mL O2k-chamber''': | |||
::::# Weigh 62.5 mg cytochrome ''c'' into a small glass beaker. Difficult to weigh, since the powder is electrostatically charged. | |||
::::# Add 1 mL H<sub>2</sub>O; ''c'' dissolves easily. | |||
::::# Divide into 0.2 mL portions. | |||
::::# Store at -20 °C. | |||
:::» '''O2k manual titrations:''' [[MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations]] | |||
::::* Titration volume ('''0.5-mL O2k-chamber'''): 1 µL using a 10 µL Hamilton syringe. | |||
::::* Final concentration: 10 µM. | |||
== DatLab oxygen flux: performance and data analysis == | |||
:::: Quality of the results are strongly affected by the performance and data analysis. By adding cytochrome ''c'' in respirometric experiments the outer mitochondrial membrane integrity can be evaluated ([[Cytochrome c control efficiency|cytochrome ''c'' control efficiency]]). The following DatLab traces illustrate examples of cytochrome ''c'' addition: | |||
<gallery mode=default perrow=2 widths="600px" heights="400px"> | |||
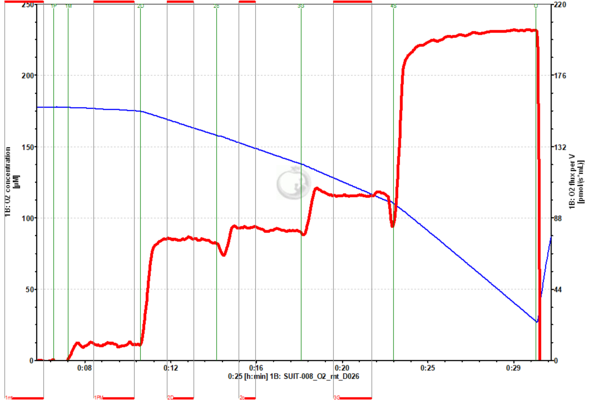
File:cyt_c_traces_O2_flux_01.png | '''Figure 1'''. Cytochrome ''c'' addition (2c) in OXPHOS state, using pyruvate and malate as NADH-linked substrates. An increase in oxygen flux per volume (red trace, right axis) can be seen upon cytochrome ''c'' addition ([[Cytochrome c control efficiency|cytochrome ''c'' control efficiency]]=0.09). Cardiac isolated mitochondria from mouse. Experiment 2019-02-19 P1-02 ([[SUIT-008_O2_mt_D026|SUIT-008 O2 mt D026]], DatLab 7.4). | |||
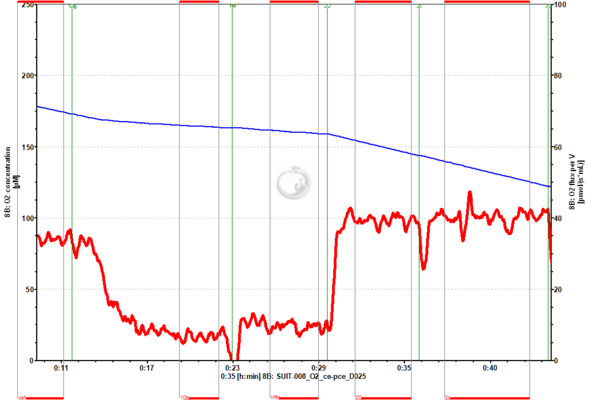
File:cyt_c_traces_O2_flux_02.png | '''Figure 2'''. Example of cytochrome ''c'' addition (2c) in OXPHOS state, in the presence of pyruvate and malate as NADH-linked substrates. The ([[Cytochrome c control efficiency|cytochrome ''c'' control efficiency]]=0.02) indicates that cryopreservation, sample preparation and the use of the detergent [[Digitonin|digitonin]] did not affect the integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2017-02-08 P1-02 ([[SUIT-008_O2_ce-pce_D025|SUIT-008 O2 ce-pce D025]], DatLab 7.4). | |||
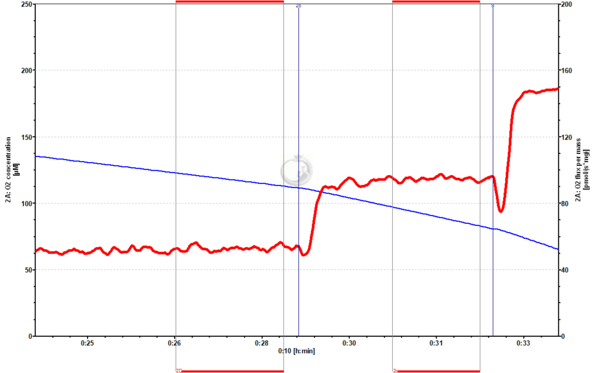
File:cyt_c_traces_O2_flux_03.png | '''Figure 3'''. Cytochrome ''c'' addition (2c) in OXPHOS state (in the presence of pyruvate, glutamate and malate) triggers an increase of the oxygen flux. This high [[Cytochrome c control efficiency|cytochrome ''c'' effect]] (0.44) may indicate a lost of the outer mitochondrial membrane integrity due to 1) sample preparation or 2) treatment (see [[Cytochrome c control efficiency#Cytochrome_c_release|cytochrome ''c'' release]]). BAT tissue homogenate from mouse. Experiment 2015-07-09-P2-03. | |||
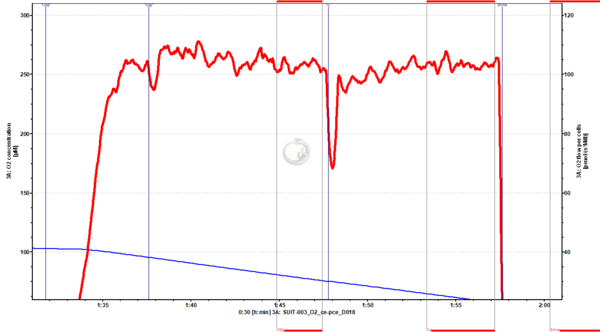
File:2019-08-06 P3-02 - A - for cyt c page.png | '''Figure 4'''. Cytochrome ''c'' addition (1c) in OXPHOS state (in the presence of succinate and rotenone) seems to trigger at first a decrease in oxygen flux, and then an increase up to the same levels as before. It is important to wait for the stabilization of the oxygen flux to set the mark, avoiding an artefactual negative [[Cytochrome c control efficiency|cytochrome ''c'' effect]] (in this case, the cytochrome ''c'' control efficiency was 0.001). Huh 7 cells, permeabilized with digitonin. Experiment 2019-08-06 P3-02. | |||
|- | |||
</gallery> | |||
::: See also: [[Steady_state#OXPHOS_state|Steady state]], Figures 1-3. | |||
::::* ''For further information see:'' » [[Cytochrome c control efficiency]] | |||
{{Keywords: DatLab performance and data analysis}} | |||
== | == [[SUITbrowser]] question: mt outer membrane integrity == | ||
:::: The cytochrome ''c'' test is available at several [[SUIT]] protocols. The [https://suitbrowser.oroboros.at/ SUITbrowser] shows which protocols contain this test, alongside answer other research questions. | |||
Latest revision as of 09:37, 4 April 2024
Description
Cytochrome c is a component of the Electron transfer-pathway (Electron transfer pathway) in mitochondria. It is a small heme protein loosely associated with the outer side of the inner mitochondrial membrane. The heme group of cytochrome c transfers electrons from Complex III to Complex IV. The release of cytochrome c into the cytoplasm is associated with apoptosis. Cytochrome c is applied in HRR to test the integrity of the mitochondrial outer membrane (cytochrome c control efficiency).
Abbreviation: c
Reference: MiPNet09.12; Gnaiger 2002 Biochem Soc Trans
MitoPedia topics: Substrate and metabolite
Application in HRR: storage and stock solution of c
- c: Cytochrome c (from equine heart; small hemeprotein), Sigma-Aldrich: C7752, store at -20 °C, CAS: 9007-43-6, M = 12,384 g·mol-1
- The cytochrome c recommended (C7752, cytochrome c from equine heart) is out of stock for the next months (estimated delivery on November 25, 2021). The use of other cytochrome c sources is discussed in the MiPNet discussion forum.
- c: Cytochrome c (from equine heart; small hemeprotein), Sigma-Aldrich: C7752, store at -20 °C, CAS: 9007-43-6, M = 12,384 g·mol-1
- Preparation of 4 mM cytochrome c solution (dissolved in H2O) for 2-mL O2k-chamber:
- Weigh 50 mg cytochrome c into a small glass beaker. Difficult to weigh, since the powder is electrostatically charged.
- Add 1 mL H2O; c dissolves easily.
- Divide into 0.2 mL portions.
- Store at -20 °C.
- » O2k manual titrations: MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
- Titration volume (2-mL O2k-chamber): 5 µL using a 25 µL Hamilton syringe.
- Final concentration: 10 µM.
- Preparation of 5 mM cytochrome c solution (dissolved in H2O) for 0.5-mL O2k-chamber:
- Weigh 62.5 mg cytochrome c into a small glass beaker. Difficult to weigh, since the powder is electrostatically charged.
- Add 1 mL H2O; c dissolves easily.
- Divide into 0.2 mL portions.
- Store at -20 °C.
- Preparation of 5 mM cytochrome c solution (dissolved in H2O) for 0.5-mL O2k-chamber:
- » O2k manual titrations: MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
- Titration volume (0.5-mL O2k-chamber): 1 µL using a 10 µL Hamilton syringe.
- Final concentration: 10 µM.
DatLab oxygen flux: performance and data analysis
- Quality of the results are strongly affected by the performance and data analysis. By adding cytochrome c in respirometric experiments the outer mitochondrial membrane integrity can be evaluated (cytochrome c control efficiency). The following DatLab traces illustrate examples of cytochrome c addition:
Figure 1. Cytochrome c addition (2c) in OXPHOS state, using pyruvate and malate as NADH-linked substrates. An increase in oxygen flux per volume (red trace, right axis) can be seen upon cytochrome c addition (cytochrome c control efficiency=0.09). Cardiac isolated mitochondria from mouse. Experiment 2019-02-19 P1-02 (SUIT-008 O2 mt D026, DatLab 7.4).
Figure 2. Example of cytochrome c addition (2c) in OXPHOS state, in the presence of pyruvate and malate as NADH-linked substrates. The (cytochrome c control efficiency=0.02) indicates that cryopreservation, sample preparation and the use of the detergent digitonin did not affect the integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane. Cryopreserved HEK-293 cells. Experiment 2017-02-08 P1-02 (SUIT-008 O2 ce-pce D025, DatLab 7.4).
Figure 3. Cytochrome c addition (2c) in OXPHOS state (in the presence of pyruvate, glutamate and malate) triggers an increase of the oxygen flux. This high cytochrome c effect (0.44) may indicate a lost of the outer mitochondrial membrane integrity due to 1) sample preparation or 2) treatment (see cytochrome c release). BAT tissue homogenate from mouse. Experiment 2015-07-09-P2-03.
Figure 4. Cytochrome c addition (1c) in OXPHOS state (in the presence of succinate and rotenone) seems to trigger at first a decrease in oxygen flux, and then an increase up to the same levels as before. It is important to wait for the stabilization of the oxygen flux to set the mark, avoiding an artefactual negative cytochrome c effect (in this case, the cytochrome c control efficiency was 0.001). Huh 7 cells, permeabilized with digitonin. Experiment 2019-08-06 P3-02.
- See also: Steady state, Figures 1-3.
- For further information see: » Cytochrome c control efficiency
- See also: Steady state, Figures 1-3.
- Bioblast links: DatLab performance and data analysis - >>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>
- Performance
- » Smoothing
- » Reoxygenations
- » Steady state
- » Sample addition
- » ROUTINE
- » ADP
- » Cytochrome c
- » Succinate
- » Oligomycin
- » Uncoupler
- » Rotenone
- » Antimycin A
- » Complex IV
- Performance
- Data analysis
- » Smoothing
- » Reoxygenations
- » Steady state
- » Sample addition
- » ROUTINE
- » ADP
- » Cytochrome c
- » Succinate
- » Oligomycin
- » Uncoupler
- » Rotenone
- » Antimycin A
- » Complex IV
- Data analysis
SUITbrowser question: mt outer membrane integrity
- The cytochrome c test is available at several SUIT protocols. The SUITbrowser shows which protocols contain this test, alongside answer other research questions.