Description
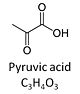
Pyruvic acid, C3H4O3, is an alpha-keto monocarboxylic acid which occurs under physiological conditions mainly as the anion pyruvate-, P, with pKa = 2.5. Pyruvate is formed in glycolysis from phosphoenolpyruvate. In the cytosol, pyruvate is a substrate of lactate dehydrogenase. Pyruvate enters the mitochondrial matrix via a specific low Km' H+/monocarboxylate cotransporter known as the pyruvate carrier. Similarly, the plasma membrane of many cell types has H+/monocarboxylate cotransporter activity and pyruvate can thus be added as a substrate to living cells. In the mt-matrix the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate is catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase and yields acetyl-CoA. Pyruvate competitively reverses the inhibition of cytochrome c oxidase by cyanide. Pyruvate is an antioxidant reacting with hydrogen peroxide.
Abbreviation: P
Reference: Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways, MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
Application in HRR
- P: Pyruvate (pyruvic acid, sodium salt; C3H3O3Na), Sigma-Aldrich: P2256, store at 4 °C, CAS: 113-24-6, M = 110.0 g·mol-1
- Hazard statements: H317, H319; may cause an allergic skin reaction, causes serious eye irritation
- P: Pyruvate (pyruvic acid, sodium salt; C3H3O3Na), Sigma-Aldrich: P2256, store at 4 °C, CAS: 113-24-6, M = 110.0 g·mol-1
- It is possible to weigh the powder beforehand in the Eppendorf-type tubes and store these tubes at 4 °C, to be diluted only on the day of use.
- After addition of H2O the pH of the Pyruvate solution is about 6. This is acceptable without pH-adjustment, because the titrated volumes are small and reaction media are buffered.
- 2021-03: The preparation instructions were updated to take the volume of the solute (P) into account (see: Volume of the solute). The concentrations prepared following the former instructions (see Discussion section) are sufficiently high for SUIT protocol titrations.
- Preparation of 2 M stock solution (200 µL, dissolved in H2O) for use in 2-mL O2k-chamber:
- Prepare fresh everyday.
- Weigh 44 mg of pyruvic acid directly into a 0.5 mL Eppendorf tube.
- Add 180 µL H2O.
- » O2k manual titrations MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
- Titration volume (2-mL O2k-chamber): 5 µL using a 25 µL Hamilton syringe.
- Final concentration: 5 mM.
- Preparation of 2.5 M stock solution (200 µL, dissolved in H2O) for use in 0.5-mL O2k-chamber:
- Prepare fresh everyday.
- Weigh 55 mg of pyruvic acid directly into a 0.5 mL Eppendorf tube.
- Add 175 µL H2O.
- » O2k manual titrations MiPNet09.12 O2k-Titrations
- Titration volume (0.5-mL O2k-chamber): 1 µL using a 10 µL Hamilton syringe.
- Final concentration: 5 mM.
Troubleshooting
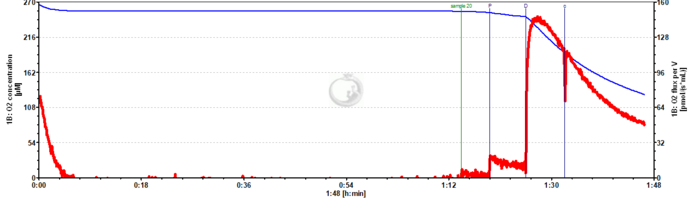
Unstable respiration while using pyruvate as the only substrate
- Customer ID: AU Melbourne White C
- Question:
- I am evaluating mitochondrial respiration from Drosophila melanogaster using Pyruvate, ADP, and Cytochrome C. However, I do not achieve a steady state level in OXPHOS.
- Any advice would be appreciated. The data is attached (2019-07-17).
- Answer:Pyruvate alone is not sufficient to support NADH-linked respiration. In order to do so you need to combine pyruvate with at least a second NADH-linked substrate (e.g. Malate) or use a more complex combination of substrates (e.g., Pyruvate&Glutamate&Malate). See Fig. 5.9. in Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways
- Additionally, you may consult some of the publications from Drosophila melanogaster mitochondria: O2k-Publications:_Drosophila
MitoPedia topics:
Substrate and metabolite