Difference between revisions of "SUIT-011"
From Bioblast
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
{{#ask:[[Category:Publications]] [[Additional label::SUIT-011]] | {{#ask:[[Category:Publications]] [[Instrument and method::O2k-Protocol]] [[Additional label::SUIT-011]] | ||
|?Was published in year=Year | |?Was published in year=Year | ||
|?Has title=Reference | |?Has title=Reference | ||
Revision as of 17:46, 15 January 2019
Description
Abbreviation: NS(GM)
Reference: A ![]() »Versions
»Versions
- SUIT-category: NS(GM)
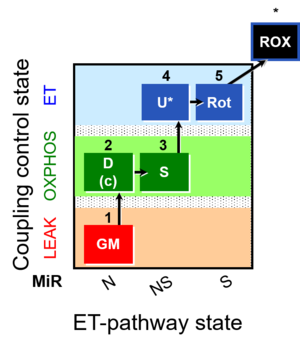
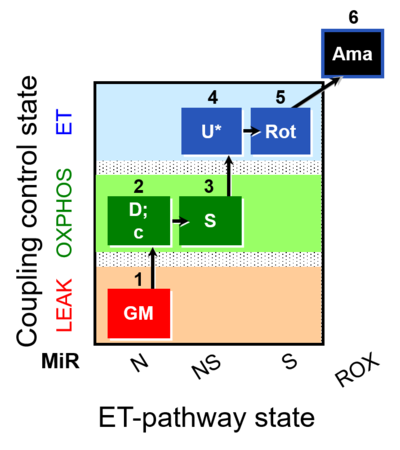
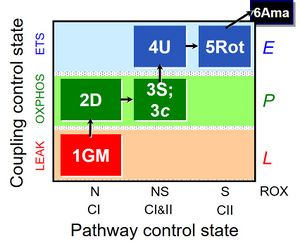
- SUIT protocol pattern: diametral 1GM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot;6Ama
References
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1GM | GML(n) | N | CI | 1GM
|
| 2D | GMP | N | CI | 1GM;2D
|
| 2c | GMcP | N | CI | 1GM;2D;2c
|
| 3S | GMSP | NS | CI&II | 1GM;2D;2c;3S
|
| 4U | GMSE | NS | CI&II | 1GM;2D;2c;3S;4U
|
| 5Rot | SE | S | CII | 1GM;2D;2c;3S;4U;5Rot
|
| 6Ama | ROX | 1GM;2D;2c;3S;4U;5Rot;6Ama
|
| Step | Respiratory state | Pathway control | ET-Complex | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ## AsTm | AsTmE | CIV | CIV | |
| ## Azd | CHB |
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary
Strengths and limitations
- Comparison of GM- with PM-capacity yields important information on N-pathway respiratory control upstream of CI (Lemeux et al 2017; Votion et al 2012).
- A succinate concentration of >10 mM may be required for saturating SE capacity.
- Rox might be inhibited slightly further by inhibition of CIV by cyanide (KCN; 1 μM). But cyanide inhibits not only CIV, but also catalase and other oxygenases involved in ROX.
- + NS-OXPHOS capacity provides a physiologically relevant estimate of maximum mitochondrial respiratory capacity.
- + Glutamate is easier to prepare compared to pyruvate.
- + Application of the cytochrome c test early in the protocol ensures comparability of all states in case of any effect of c.
- + Reasonable duration of the experiment.
- - GM and PM yield typically identical fluxes in human skeletal muscle fibres. However, PM is the superior alternative to GM: the fraction of the N-pathway is lower and of the S-pathway is higher with GM compared to PM (GMP is inhibited by the CII inhibitor malonic acid to a larger extent than PMP). PM, therefore, yields a more sensitive assay for the diagnosis of injuries in the N-pathway, since an impairment of N-pathway capacity can be compensated partially by activation of the S-pathway. This is a disadvantage compared to SUIT-004 and SUIT-008 for diagnosis of N-capacity.
- - To detect an additive effect of P after GMP, pyruvate would have to be added as step 3 (before S). However, inhibition of respiration was observed after titration of P (5 mM) in horse skeletal muscle fibres (Votion et al 2012), which was not the case when P was titrated in steps of 1 mM.
- - When evaluating the additive effect of the N- and S-pathway, it has to be considered that NSP- and NSE-capacities can only be compared with NP- and SE-capacities. This is not a problem when NSP = NSE (Gnaiger 2009). Otherwise, it may be assumed that SP = SE (Votion et al 2012), such that NSP can be compared with NP + SP. SUIT-004 should be chosen for the additive effect in the ET-state.
- - Rox may be lower in substrate states earlier in the SUIT protocol. Therefore, this Rox measurement is frequently taken as a methodological control rather than as the final basis of Rox correction of mitochondrial respiration (mt).
- - Careful washing is required after the experiment to avoid carry-over of inhibitors and uncoupler.
- - CIV activity is not measured, to save experimental time.
Compare SUIT protocols
- GM and PM yield typically identical fluxes in human skeletal muscle fibres.
- SUIT-004 1PM;2D;3U;4S;5Rot-
- SUIT-008 1PM;2D;3G;4S;5U;6Rot-
- 1PM;2D;3U;4G;5S;6Oct;7Rot;8Gp-
- 1PGM;2D;3S;4U;5Rot-
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
SUIT protocol,
Recommended
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry