Difference between revisions of "PGM-pathway control state"
Beno Marija (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
'''SUIT protocol:''' [[SUIT-001]], [[SUIT-012]], [[SUIT-014]] | '''SUIT protocol:''' [[SUIT-001]], [[SUIT-012]], [[SUIT-014]] | ||
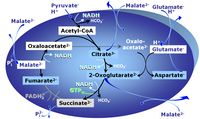
[[Pyruvate]] (P) is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl-CoA and CO<sub>2</sub>, yielding [[NADH]] catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase. [[Malate]] (M) is oxidized to oxaloacetate by mt-malate dehydrogenase located in the mitochondrial matrix. Condensation of oxaloacate with acetyl-CoA yields citrate (citrate synthase). Glutamate&malate is a substrate combination supporting an N-linked pathway control state, when glutamate is transported into the mt-matrix via the [[glutamate-aspartate carrier]] and reacts with [[oxaloacetate]] in the [[transaminase]] reaction to form [[aspartate]] and [[oxoglutarate]]. Glutamate as the sole substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate<sup>-</sup>/OH<sup>-</sup> exchanger, and is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix by [[glutamate dehydrogenase]] to α-ketoglutarate ([[oxoglutarate | 2-oxoglutarate]]), representing the [[glutamate anaplerotic pathway control state]]. 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) is formed from isocitrate (isocitrate dehydrogenase, from oxaloacetate and glutamate by the transaminase, and from glutamate by the glutamate dehydrogenase. | [[Pyruvate]] (P) is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl-CoA and CO<sub>2</sub>, yielding [[NADH]] catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase. [[Malate]] (M) is oxidized to oxaloacetate by mt-malate dehydrogenase located in the mitochondrial matrix. Condensation of oxaloacate with acetyl-CoA yields citrate (citrate synthase). Glutamate&malate is a substrate combination supporting an N-linked pathway control state, when glutamate is transported into the mt-matrix via the [[glutamate-aspartate carrier]] and reacts with [[oxaloacetate]] in the [[transaminase]] reaction to form [[aspartate]] and [[oxoglutarate]]. Glutamate as the sole substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate<sup>-</sup>/OH<sup>-</sup> exchanger, and is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix by [[glutamate dehydrogenase]] to α-ketoglutarate ([[oxoglutarate | 2-oxoglutarate]]), representing the [[glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state]]. 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) is formed from isocitrate (isocitrate dehydrogenase, from oxaloacetate and glutamate by the transaminase, and from glutamate by the glutamate dehydrogenase. | ||
|info=[[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways |Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways - Chapter 5.3]] | |info=[[Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways |Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways - Chapter 5.3]] | ||
}} | }} | ||
Revision as of 11:30, 3 June 2020
Description
PGM: Pyruvate & Glutamate & Malate.
MitoPathway control state: NADH Electron transfer-pathway state
SUIT protocol: SUIT-001, SUIT-012, SUIT-014
Pyruvate (P) is oxidatively decarboxylated to acetyl-CoA and CO2, yielding NADH catalyzed by pyruvate dehydrogenase. Malate (M) is oxidized to oxaloacetate by mt-malate dehydrogenase located in the mitochondrial matrix. Condensation of oxaloacate with acetyl-CoA yields citrate (citrate synthase). Glutamate&malate is a substrate combination supporting an N-linked pathway control state, when glutamate is transported into the mt-matrix via the glutamate-aspartate carrier and reacts with oxaloacetate in the transaminase reaction to form aspartate and oxoglutarate. Glutamate as the sole substrate is transported by the electroneutral glutamate-/OH- exchanger, and is oxidized in the mitochondrial matrix by glutamate dehydrogenase to α-ketoglutarate ( 2-oxoglutarate), representing the glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state. 2-oxoglutarate (α-ketoglutarate) is formed from isocitrate (isocitrate dehydrogenase, from oxaloacetate and glutamate by the transaminase, and from glutamate by the glutamate dehydrogenase.
Abbreviation: PGM
Reference: Gnaiger 2014 MitoPathways - Chapter 5.3
MitoPedia concepts:
SUIT state
PGML
PGM pathway in the LEAK state can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocols:
PGMP
PGM pathway in the OXPHOS state can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocols:
-
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized fibers (pfi): SUIT-008 O2 pfi D014
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): SUIT-008 O2 ce-pce D025
-
PGME
PGM pathway in the ET state can be evaluated in the following SUIT protocols:
-
- DL-Protocol for isolated mitochondria and tissue homogenate (mt):SUIT-001 O2 mt D001
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized fibers (pfi):SUIT-001 O2 pfi D002
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized cells (pce): SUIT-001 O2 ce-pce D003
- DL-Protocol for permeabilized PBMC and PLT: SUIT-001 O2 ce-pce D004
-