Description
Reference: A: quality control evaluation of mitochondrial preparations - SUIT-029
MitoPedia concepts:
MiP concept,
SUIT protocol,
Recommended
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry
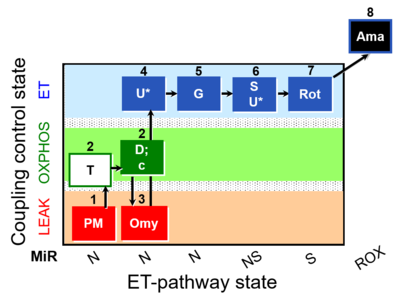
- SUIT protocol pattern: 1PM;2D;3Omy;4U-
The SUIT-029 protocol is specially designed to evaluate the quality of mitochondrial preparations in a wide variety of species, tissues and cell types. SUIT-029 gives information of the linear coupling control (L- P- E) with NADH linked-substrates (PM). With this protocol ATPase contamination and mitochondrial outer membrane integrity in different mitochondrial preparations with N substrates can be evaluated. Moreover, the LEAK state L(Omy) without the uncoupling promoted by the ATPase contamination and as a control with the L(n) previously obtained is also assessed. As a test for limitation of OXPHOS capacity by the phosphorylation system relative to ET-capacity the performance of uncoupler titrations might be carried out with N in order to calculate ET-coupling efficiency (1-L/E). The additive effect of convergent flux through NADH-linked respiration, NS, and S in E can be evaluated by using this protocol.
Communicated by Antunes D, Komlodi T, Gnaiger E (last update 2020-03-06)
Specific SUIT protocols
SUIT-029 O2 mt D066
- SUIT-029 O2 mt D066 for isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenate and permeabilized cells (already permeabilized when they are added to the chamber)
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M)
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PM | PML(n) | N | CI | 1PM
|
| 2T | PML or PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2T
|
| 2D | PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D
|
| 2c | PMcP | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D;2c
|
| 3Omy | PMLOmy | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c;3Omy
|
| 4U | PME | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U
|
| 5G | PGME | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G
|
| 6S | PGMSE | NS | CI+CII | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S
|
| 6U | PGMSE | NS | CI+CII | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S;6U
|
| 7Rot | SE | S | CI | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S;6U;7Rot
|
| 8Ama | ROX | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S;6U;7Rot;8Ama
|
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary
Strengths and limitations
- This protocol allows to evaluate the quality of mitochondrial preparations taking into account the presence of ATPases.
- + Linear coupling control (L-P-E) with N substrates (PM). N substrates (PM) make use of all the proton pumps in the ETS without the additivity effect of the S-pathway, which would decrease the coupling degree. Additionally, PM is the superior alternative to GM: the fraction of the N-pathway is lower and S-pathway contribution is higher with GM compared to PM. PM, therefore, yields a more sensitive assay for the diagnosis of injuries in the N-pathway, since impairment of N-pathway capacity can be compensated partially by activation of the S-pathway.
- +OXPHOS capacity evaluation is included (2D).
- + Evaluation of the ATPase contamination is included (2T).
- + The integrity of mitochondrial outer membrane is assessed ( 2c).
- + LEAK respiration overestimation is prevented in the presence of Oligomycin, without the uncoupling promoted by the ATPase contamination and as a control with the L(n) previously obtained.
- + Internal ET-pathway control step is included as a test for limitation of OXPHOS-capacity by the phosphorylation system relative to ET-capacity. The evaluation of ET-state with NADH-linked substrates allows to calculate ET-coupling efficiency (1-L/E).
- + The additive effect of convergent flux through NADH-linked respiration in ET-state is evaluated (5G).
- + ET-state with NS-linked substrates is evaluated (5S) followed by additional U titration to ensure ET-capacity.
- + Assessment of ET-capacity not only in N- and NS-pathway but also in S-pathway (7Rot).
- + This protocol can be optionally harmonized with many other SUIT protocols (e.g., SUIT-001, SUIT-004, SUIT-008). Addition of G in NADH-supported OXPHOS enables evaluation of the glutamate anaplerotic pathway control state.
- + This protocol can be extended with the Complex IV module.
- - Long duration of the experiment due to adjustment of Oligomycin concentration (in the case of a new isolation protocol). For a shorter protocol the titration of glutamate, succinate and rotenone could be omitted.
- - The use of Oligomycin could affect the evaluation of the ET capacity (could inhibit ET-state).
- - F-pathway is not analysed.
- - Careful washing is required after the experiment to avoid carry-over of inhibitors and uncoupler.
Compare SUIT protocols
- SUIT-001 O2 mt D001 (RP1): Harmonized SUIT protocol for isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenate and permeabilized cells (already permeabilized).
- SUIT-002 O2 mt D005 (RP2): Harmonized SUIT protocol for isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenate and permeabilized cells (already permeabilized).